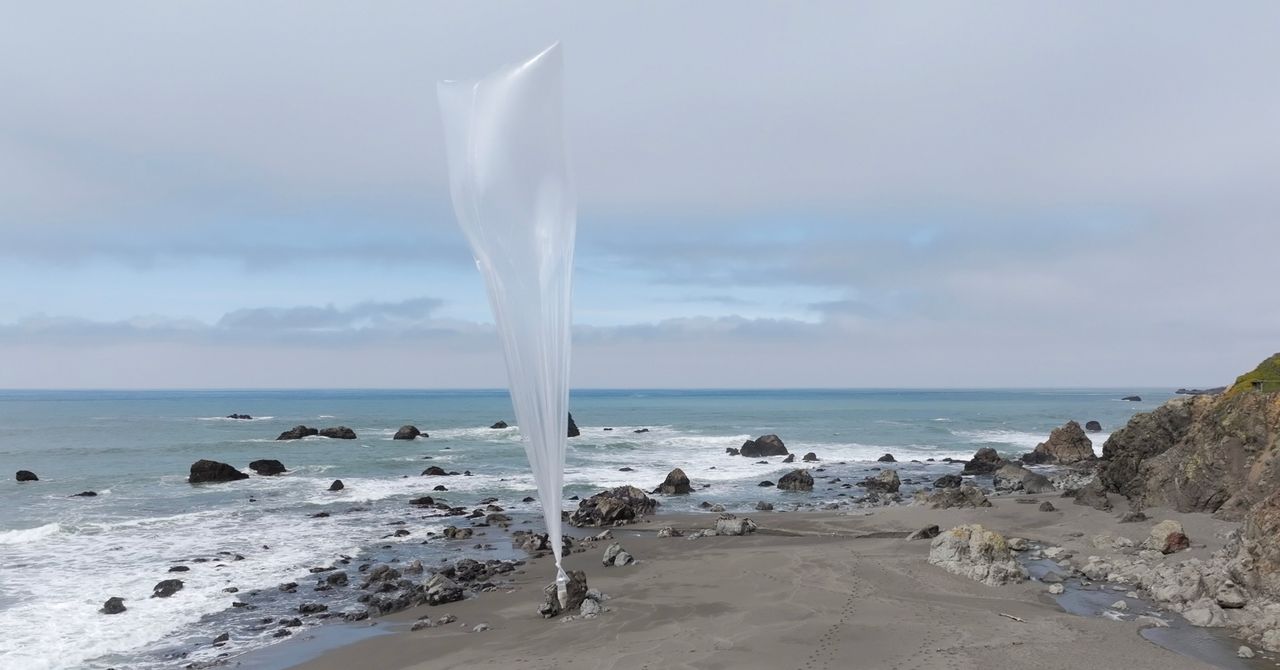
Windborne balloon, on the other hand, can collect and distribute data from distant regions. This makes them more adaptive and useful especially to monitor atmospheric rivers that bring an extreme precipital to coastal regions, said Glackin. “I am like seeing them in the continuation of observation systems.”
The company deploys around 100 balloons from six launch sites around the world, a fiction of the 92 launch sites operated by the NOAA, but it aims to develop to launch up to 10,000 balls over the next five years, said Dean.
Windborne data is less expensive to thank “for an observation or for the station,” wrote Curtis Marshall, director of the commercial data program for the NWS, in an email.
And although its data is now free and open to the public, as the company is developing, it wants to retain some of the information it brings together for 48 hours so that it can return it to private buyers, said Dean. These data would no longer be useful to other forecasters.
Old School technology of radiosondes is difficult to replace
The radiosonds collect a vertical profile – a ground level line to the point where the ball explodes – from D given in the atmosphere, which is important to understand the signals of climate change. Windborne’s balloon, on the other hand, collect thousands of data points, at different altitudes, through a horizontal extent. Their path is somewhat ad hoc, determined by the place where the wind blows them, where the radiosonds collect data in a line rising from a location which remains the same for each launch.
Although the lack of coherent route of Windborne does not matter for short -term weather forecasts, it may be important to highlight the longer climate changes, which are currently based on decades of vertical profile data collected in the same place, said Glackin. Windborne data would not be comparable to this historic folder.
“We have a very linked climate file that went to talk about how the climate changes,” she said. “If all the radiosonds disappeared tomorrow, it would be difficult to understand what has changed, and what to attribute to technology compared to what really happened in the atmosphere.”
There are transitional methods towards a new institution, Colman, the meteorologist who worked at the NOAA, said, but the NWS needs to proactively plan this change to maintain a coherent data recording.
The NWS does not move to replace the radiosonds – but – but it is at the “first stages” of planning a new suite of observation systems of the Haute Atmospherique which would try “a lot similar to the Federal Radiosonde network”, wrote Marshall.
The new observing systems would be such as balloons, drones and planes operated by Mercally, and “complete our network of federal balloons”.
However, Austin Tindle, in the co -founder of Sorcerer, a competitor through the wind, said that the NOAA officials asked him for inclusion “what he looks like a real replacement of a rotisondi”.
“It was a change of atmosphere recently, coming to a conversation in Lot,” he said.
The dean of Windborne refused to answer when he was asked if he had had similar conversations.
The NOAA partnership with Windborne “Cound is completely up [meaning an add-on rather than a replacement]But people do not have much confidence in the wider strategy for the Noaa weather company, on the basis of everything that happened, “said Di Liberto, on June 25 of the agency appointment That it ended permanently – without five days – a Vital microwave satellite program Used for the forecast of hurricanes.