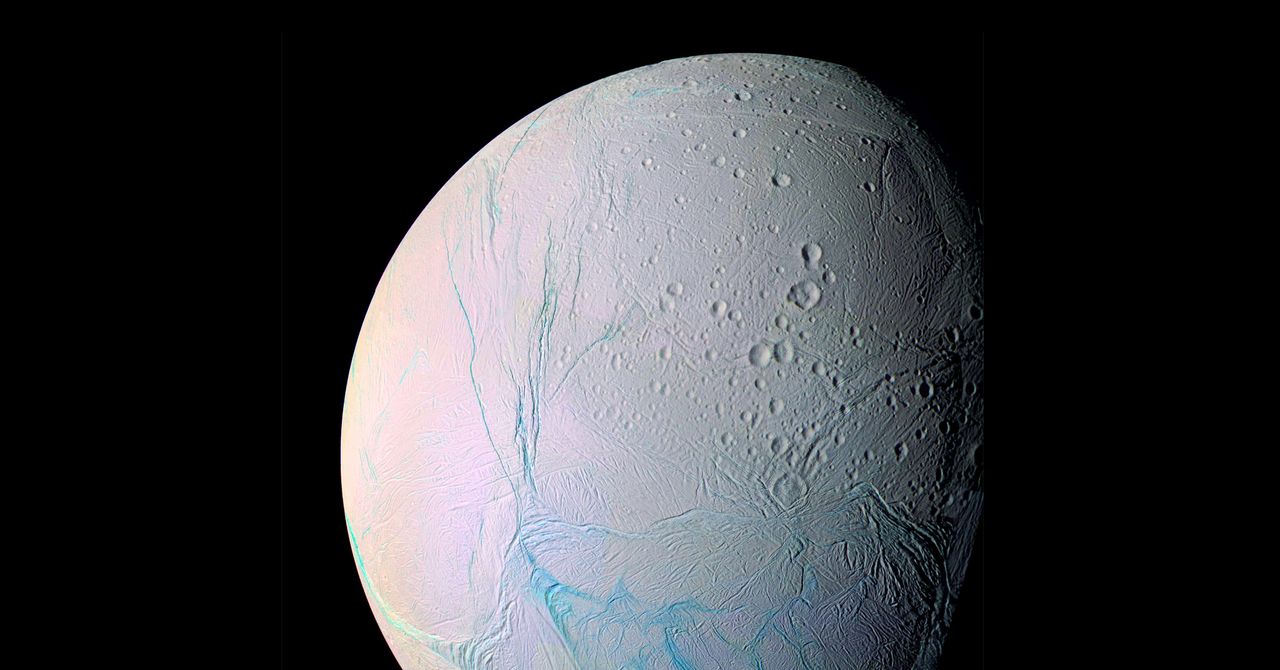
A recent study of Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons, detected several organic compounds that had never been recorded there before. The results, published this month in Natural astronomyprovide new clues about the internal chemical composition of this icy world, as well as new hope that it could support life.
The researchers analyzed data from Cassini probe, launched in 1997 and which studied Saturn and its moons for years until its destruction in 2017. For Enceladus, Cassini gathered data from ice fragments forcibly ejected from the moon’s underground ocean into space.
Enceladus is one of 274 bodies discovered so far under Saturn’s gravitational pull. It measures approximately 500 kilometers in diameter, making it the sixth largest satellite on the planet. Although this moon is not notable for its size, it is notable for its cryovolcanoes, geysers located at the south pole of Enceladus that spew water vapor and ice fragments. Plumes of ejected material can extend to almost 10,000 kilometers in lengthis more than the distance between Mexico and Patagonia, and part of this material rises into space. Saturn’s outermost main ring, its E ring, is made primarily of ice ejected into space by Enceladus.
This material is believed to come from a saline water chamber beneath the moon’s icy crust and connected to its rocky core. It is possible for chemical reactions to occur there, under high pressure and heat.
Until now, most chemical analyzes of Enceladus’ ice have focused on particles deposited in Saturn’s E ring. But during a high-speed flyby of the Moon in 2008, Cassini had the chance to directly sample fragments freshly ejected from a cryovolcano. The new research paper reanalyzed this data, confirming the presence of previously detected organic molecules, as well as revealing compounds that had not previously been detected.
“Such compounds are thought to be intermediates in the synthesis of more complex molecules, which could be potentially biologically relevant. It is important to note, however, that these molecules can also be formed abiotically,” Nozair Khawaja, a planetary scientist at Freie Universität Berlin and lead author of the study, told Reuters. The discovery significantly expands the range of organic molecules confirmed on Enceladus.
The key is that the compounds appeared in freshly ejected particles, suggesting that they formed in the Moon’s hidden ocean or in contact with its internal interfaces, not during their travel through the E ring or by exposure to the conditions of space. This strengthens the hypothesis that hydrothermal processes beneath Enceladus’ surface could generate rich organic chemistry. By combining this new research with previous studies, scientists have now discovered five of the six elements essential for life (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur) in the material ejected from the satellite.
It is not in itself a discovery of life, nor of biosignatures, the signs of life. However, research confirms that Enceladus has the three basic conditions necessary for life to form: liquid water, an energy source, and essential, organic elements. “Enceladus is, and should be classified, as the primary target for exploring habitability and investigating whether there is life or not,” Khawaja said.
This story was originally published on CABLE in Spanish and was translated from Spanish.